Environment-Friendly Electromagnetic-Based Solutions for the Cotton Leaf Worm in Egypt
Funded by Information Technology Academia Collaboration (ITAC)


Project Duration: October 2019 – September 2020 (12 months)
Project Budget: EGP 250,000
Project Executive Summary:
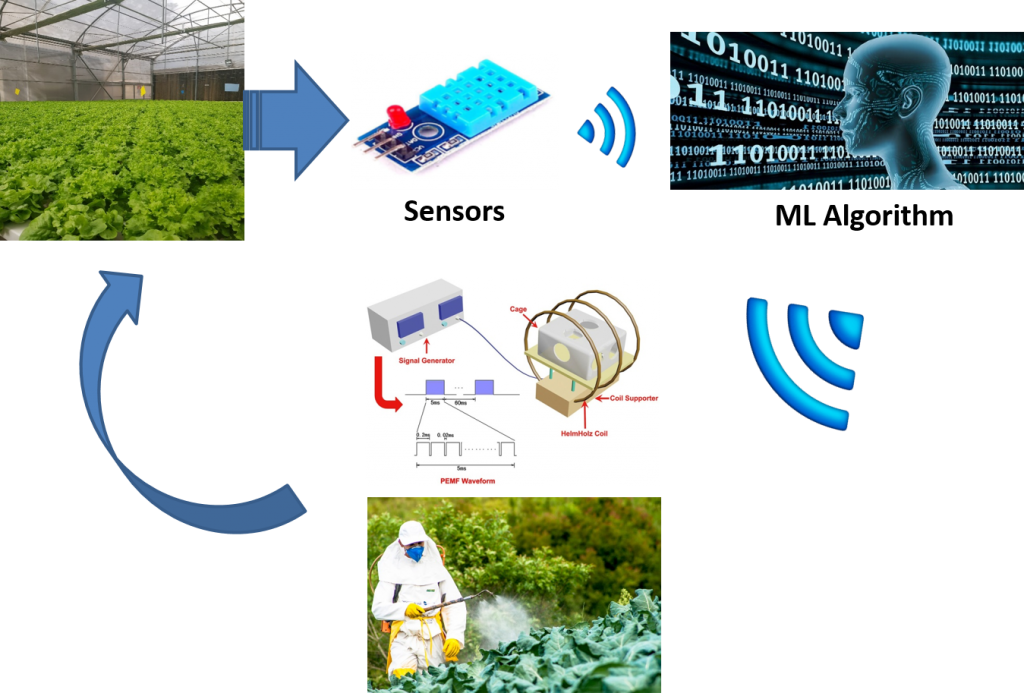
The general scope of the proposed project lies in the field of agricultural development by using green electromagnetic-based techniques. In particular, the project focuses on the early control of the harmful green field living organisms by using quasi-stationary magnetic fields. In this project, the authors target the eggs of cotton leaf worm, scientifically known as Spodoptera littoralis. The Egyptian cotton leaf worm is widely spread in Mediterranean regions and has major harmful effects on a wide range of cultivation. Its larval stage causes highly economic losses for many different types of plants. This harmful pest is very resistant to be controlled by the common chemical insecticides. Therefore, the use of electromagnetic-based technology to control the agricultural pests could provide an alternative with merits to the common used techniques.
Smart greenhouses and greenhouse automation system are new terms which newly introduced in the agricultural field to denote the implementation of technology in the traditional farming methods. The benefits of this application are multifold including improving the productivity of the farm. One important issue in the farming process is pests control in order to protect the crop from their damages effects. For effective pest control, smart greenhouse designs should include sensors for pest detection and system for pest control and eradication. In the current project we aim to construct a complete system for pest control which includes sensors supporting a machine learning software and a novel physical method for pest control (magnetic fields).
From an environmental perspective; this is a non-invasive and green technology that will be able to protect the crops from different insect pests that will eventually lead to an increase in healthy crops yield. From the human health perspective; it will protect human from the adverse effects of chemical pesticides that have been approved to cause negative effects on plants and the human health. From the economic perspective; this technology will be more economical (cheaper) than the traditional methods of chemical pesticides. It will also decrease the number of workers and decrease the possible negative side effects of chemical treatments on these workers. Additionally, this technology could have a high degree of efficiency over the traditional methods as pests usually self-develop biological immunity against frequently used chemical compounds. From a technological perspective; in principle, this is a kind of industrial production that will be used in the agricultural field. The success of the present idea could lead to the advancement of the technology in the agricultural domain which could get back with benefits on the industrial field. The major benefits of this project are expected to positively influence the green electronics sector in the Egyptian ICT industry.
Project Team:
Project Published Journal Papers:
Project Published Conference Papers:
- A. Aaraby, M. Abdelhameed, N. Magdy, L. ‘A. Said, N. Abdelaal, Y. Tarek, S. M. Darwish, M. Fahim, and H. Mostafa, “Smart IoT Monitoring System for Agriculture with Predictive Analysis”, IEEE International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technology (MOCAST 2019), Thessaloniki, Greece, pp. 1-4, 2019. [PDF]
